New capabilities introduced in ScyllaDB Enterprise make scaling operations with Tablets up to 30X faster while reducing network costs by up to 50%
ScyllaDB just released ScyllaDB 2024.2, the first enterprise release featuring ScyllaDB’s new “tablets” replication architecture. This new architecture, which builds upon a multiyear project to implement and extend the Raft consensus protocol, enables new levels of elasticity, speed, simplicity, and efficiency.
The enterprise release offers new capabilities designed to help you reduce infrastructure costs and streamline operations:
- Tablets, a dynamic data distribution architecture that significantly improves elasticity and scalability (limited availability – details in release notes)
- File-based streaming for tablets further speeds up scaling operations (e.g., adding and removing nodes)
- Strongly consistent topology updates, authentication updates, service levels (workload prioritization)
- ZSTD-based network compression for intra-node RPC, with a shard dictionary for improved performance
- DynamoDB API (Alternator) enhancements such as role-based access control
See the release notes for details
The ScyllaDB Enterprise 2024.2 release is based on ScyllaDB 6.0; it includes *all* the features available in ScyllaDB 6.0 like:
- Tablets, a dynamic way to distribute data across nodes that significantly improves scalability
- Strongly consistent topology, Auth, and Service Level updates
In addition, 2024.2 includes enterprise-only features such as:
- Improved network compression (see below)
- File-based streaming for tablets
- A new FIPS enabled Docker Image
Related links:
- Read more about ScyllaDB Enterprise
- Get ScyllaDB Enterprise 2024.2 (customers only, or 30-day evaluation)
- Upgrade from ScyllaDB Enterprise 2024.1.x to 2024.2.y
- Upgrade from ScyllaDB Open Source 6.0 to ScyllaDB Enterprise 2024.2.x
ScyllaDB Enterprise customers are encouraged to upgrade to ScyllaDB Enterprise 2024.2, and are welcome to contact our Support Team with questions.
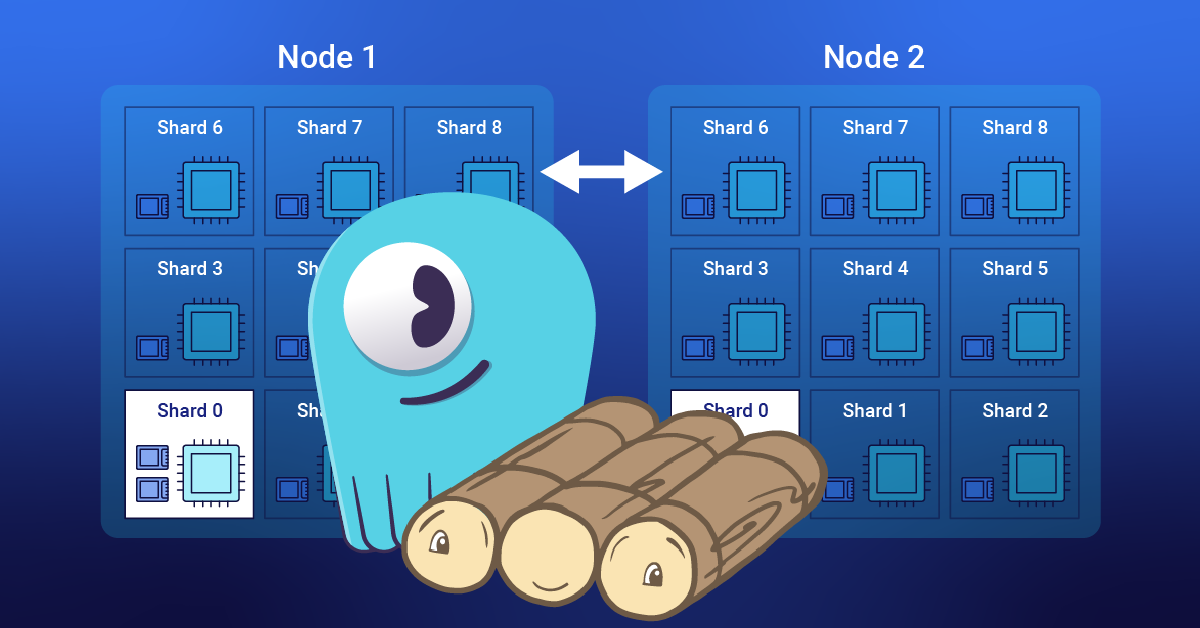
Tablets
In this release, ScyllaDB enabled Tablets, a new data distribution algorithm as a better alternative to the legacy vNodes approach inherited from Apache Cassandra.
While the vNodes approach statically distributes all tables across all nodes and shards based on the token ring, the Tablets approach dynamically distributes each table to a subset of nodes and shards based on its size. In the future, distribution will use CPU, OPS, and other information to further optimize the distribution.
In particular, Tablets provide the following:
- Faster scaling and topology changes. New nodes can start serving reads and writes as soon as the first Tablet is migrated. Together with Strongly Consistent Topology Updates (below), this also allows users to add multiple nodes simultaneously.
- Automatic support for mixed clusters with different core counts. Manual vNode updates are not required.
- More efficient operations on small tables., since such tables are placed on a small subset of nodes and shards.
Note that you can run a cluster with some of the Keyspaces with Tablets disabled, and some with tablets enabled for as long as you wish. The scaling improvement will be partial, and limited to Keyspaces with Tables enabled.
Read the Tablets documentation
Currently, tablets are ideal for new clusters that you frequently scale out or in and that have one main large table and potentially many tiny ones. ScyllaDB Support can help you determine if Tablets in release 2024.2 are a good solution for your use case.
Learn more about tablets:
- Smooth Scaling: Why ScyllaDB Moved to “Tablets” Data Distribution: The rationale behind ScyllaDB’s new “tablets” replication architecture
- ScyllaDB Fast Forward: True Elastic Scale: Introducing major architectural shifts that enable new levels of elasticity and operational simplicity
- Elasticity, Speed & Simplicity: Get the Most Out of New ScyllaDB Capabilities: A technical walkthrough of exactly what’s changed from the user/operator perspective
Monitoring Tablets
To Monitor Tablets in real time, upgrade ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack to release 4.8, and use the new dynamic Tablet panels, below.

Driver Support
The Following Drivers support Tablets
- Java driver 4.x, from 4.18.0.2
- Java driver 3.x, from 3.11.5.2
- Python driver, from 3.26.6
- Gocql driver, from 1.13.0
- Rust driver from 0.13.0
Legacy ScyllaDB and Apache Cassandra drivers will continue to work with ScyllaDB but will be less efficient when working with tablet-based Keyspaces.
Read the blog post “How We Updated ScyllaDB Drivers for Tablets Elasticity”
File based streaming for Tablets
File-based streaming is a ScyllaDB Enterprise-only feature that optimizes tablet migration.
In ScyllaDB Open Source, migrating tablets is performed by streaming mutation fragments, which involves deserializing SSTable files into mutation fragments and re-serializing them back into SSTables on the other node. In ScyllaDB Enterprise, migrating tablets is performed by streaming entire SStables, which does not require (de)serializing or processing mutation fragments. As a result, less data is streamed over the network, and less CPU is consumed, especially for data models that contain small cells.
File-based streaming is used for tablet migration in all keyspaces created with tablets enabled.
Read the file-based streaming documentation
Consistent Topology and Metadata
Strongly Consistent Topology Updates
With Raft-managed topology enabled, all topology operations are internally sequenced consistently. A centralized coordination process ensures that topology metadata is synchronized across the nodes on each step of a topology change procedure.
This makes topology updates fast and safe, as the cluster administrator can trigger many topology operations concurrently, and the coordination process will safely drive all of them to completion. For example, multiple nodes can be bootstrapped concurrently, which couldn’t be done with the previous gossip-based topology.
Strongly Consistent Topology Updates is now the default for new clusters, and should be enabled after upgrade for existing clusters.
Read the blog post “ScyllaDB’s Safe Topology and Schema Changes on Raft”
Strongly Consistent Auth Updates
System-auth-2 is a reimplementation of the Authentication and Authorization systems in a strongly consistent way on top of the Raft sub-system.
This means that Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) commands like create role or grant permission are safe to run in parallel without a risk of getting out of sync with themselves and other metadata operations, like schema changes.
As a result, there is no need to update system_auth RF or run repair when adding a Data Center.
Strongly Consistent Service Levels
Service Levels allow you to define attributes like timeout per workload. Service levels are now strongly consistent using Raft, like Schema, Topology and Auth.
Improved network compression for intra-node RPC
This release adds new Enterprise only RPC compression improvements for node to node communication:
- Using zstd instead of lz4
- Using a shared dictionary re-trained periodically on the traffic, instead of the message by message compression.
Below is a comparison of compressions algorithms on different types of data.
Note that dictionary based compression can be used with either lz4 or zstd.
The actual compression is very much workload-dependent and can vary between use cases.

Alternator Role-Based Access Control
Alternator supports Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for authorization. Control is done via the CQL API.
Native Nodetool
The nodetool utility provides simple command-line interface operations and attributes. ScyllaDB inherited the Java based nodetool from Apache Cassandra. In this release, the Java implementation was replaced with a backward-compatible native nodetool.
The native nodetool works much faster. Unlike the Java version ,the native nodetool is part of the ScyllaDB repo, and allows easier and faster updates. With the native nodetool, the JMX server has become redundant and will no longer be part of the default ScyllaDB Installation or image.
If you are using the JMX server directly, not via nodetool, you can either:
- Work directly with the ScyllaDB REST API (recommended)
- Install the JMX server yourself. See https://github.com/scylladb/scylla-jmx for instructions.
As part of moving to native tooling and away from Java tools, we will deprecate SSTableloader in future versions of ScyllaDB Enterprise. You can use the Load and Stream to upload SSTables directly to ScyllaDB, either from Apache Cassandra or other ScyllaDB clusters. We are also deprecating the Java version of nodetool, which was replaced by a compatible native version (see above).
Maintenance
Maintenance mode is a new mode in which the node does not communicate with clients or other nodes and only listens to the local maintenance socket and the REST API. It can be used to fix damaged nodes – for example, by using nodetool compact or nodetool scrub. In maintenance mode, ScyllaDB skips loading tablet metadata if it is corrupted to allow an administrator to fix it.
Also, the Maintenance Socket provides a new way to interact with ScyllaDB from within the node it runs on. It is mainly for debugging. You can use CQLSh with the Maintenance Socket as described in the Maintenance Socket docs.
Improvements and Bug Fixes
The latest release also features extensive improvements to stability, performance, monitoring and more. For details, see the release notes on the ScyllaDB Community Forum.